Cell Ranger ARC, printed on 03/03/2025
Cell Ranger ARC pipelines run on Linux systems that meet these minimum requirements:
Note: Version 2.0 is the last version that will support CentOS/RedHat 6 or Ubuntu 12.04. Future versions will require CentOS/RedHat 7 or newer, or Ubuntu 14.04 or newer.
In order to run in cluster mode, the cluster needs to meet these additional minimum requirements:
In order to run cellranger-arc mkfastq, the following software needs to be installed:
| Limit | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| user open files | 16k |
| system max files | 10k per GB RAM available to Cell Ranger ARC |
| user processes | 64 per core available to Cell Ranger ARC |
The following data is based on time trials using Amazon EC2 instances, our PBMC 10k dataset, and version 2.0 of Cell Ranger ARC. Performance is dependent on both the number of cells and the number of reads per cell. These plots will not be updated with every subsequent release of Cell Ranger ARC, unless pipeline performance changes significantly.
| Instance | Threads | Memory (GB) | Core hours | Wall time | Storage HWM (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r3.8xlarge (Ivy Bridge) | 32 | 64 | 220 | 8h 22m | 428 |
| m5.24xlarge (Skylake) | 96 | 384 | 198 | 3h 15m | 356 |
| r4.16xlarge (Broadwell) | 64 | 488 | 196 | 4h 26m | 484 |
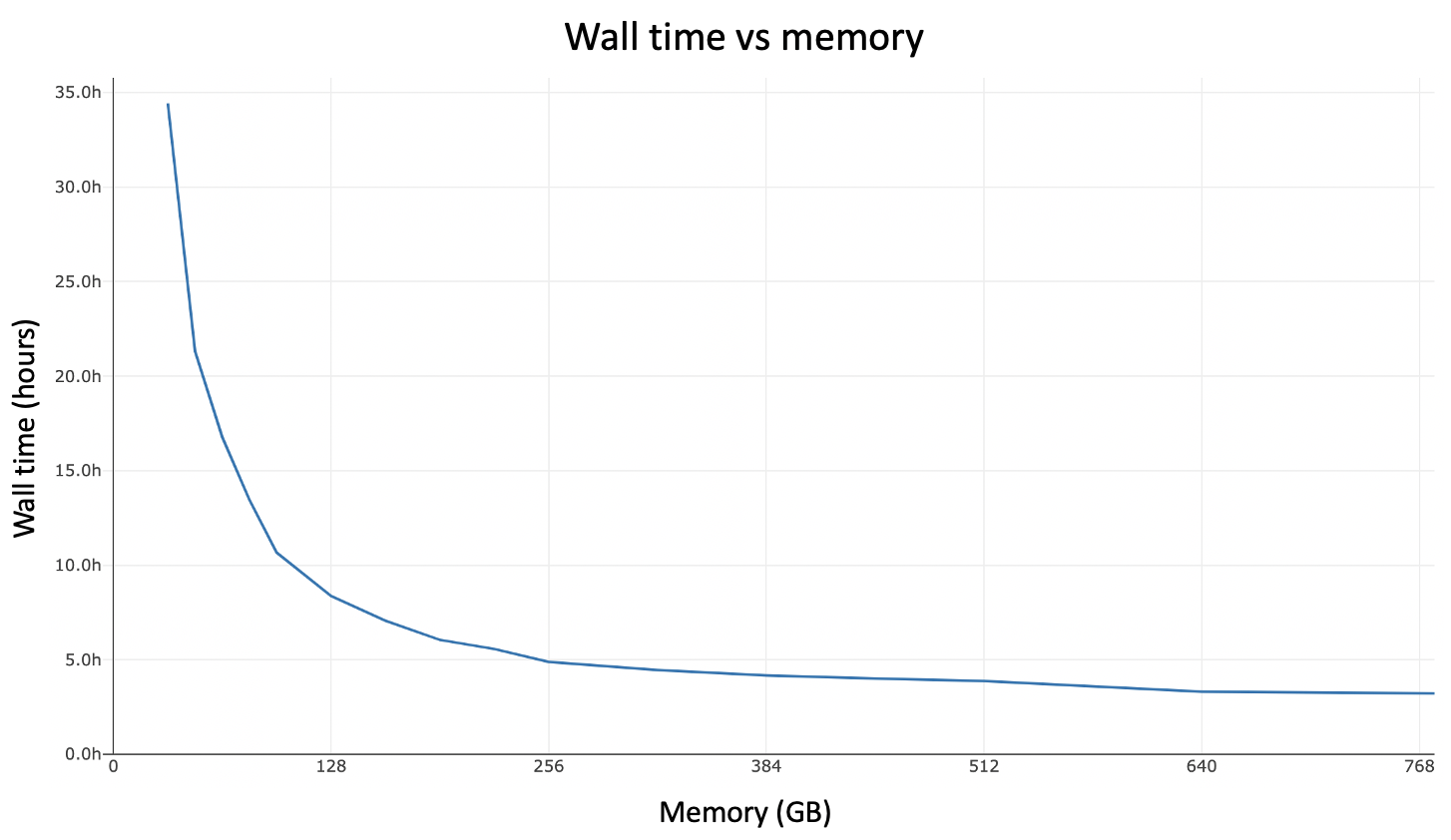
Here is cellranger-arc count walltime as a function of available memory based on the r3.8xlarge Ivy Bridge architecture. In general, you can improve performance by allocating more than the minimum 64GB of memory to the pipeline. There is notable diminishing return beyond 320GB.
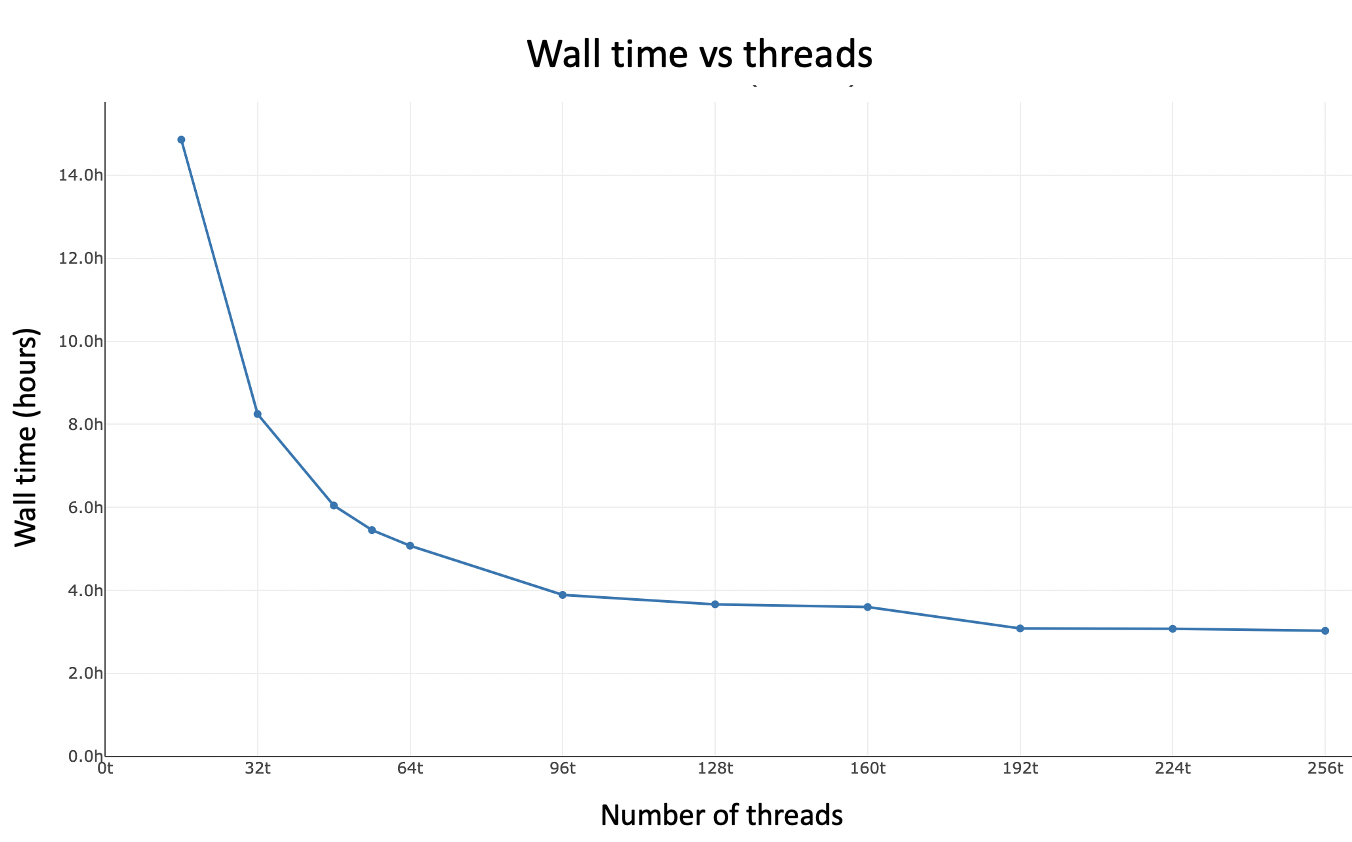
Here's cellranger-arc count walltime as a function of threads. If your system has ≫96 logical cores, you may want to run with --localcores=96 since there is diminishing return beyond 96 threads.